- The capital conservation buffer (CCB) requirement was added to the interagency capital rules after the 2007-2008 financial crisis. It requires a bank to hold at least 2.50 percentage points of common equity tier 1 capital above the minimum risk-based capital (RBC) requirements to help a bank during periods of stress. The CCB gradually restricts dividend payments and other capital distributions when a bank breaches the requirement. The maximum payout ratio declines as the CCB declines._
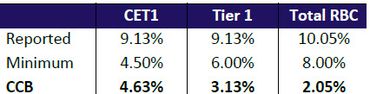
- A bank calculates its CCB by subtracting the minimum risk-based ratios from its reported ratios. The lowest amount is its CCB. In the example below, the bank’s CCB is 2.05 percent and its maximum payout of eligible retained income is 60 percent. Qualifying community banking organizations (CBOs)_ that elect the Community Bank Leverage Ratio Framework (CBLR), which went into effect in 2020, do not report RBC ratios or a CCB. The number of banks reporting the CCB has greatly declined since the introduction of the CBLR; approximately 62 percent of CBOs reported the CCB (2,413) as of September 30, 2023.
- Since the CCB was fully phased-in, the percentage of CBOs that are below the minimum CCB requirement has increased from 0.48 percent of reporting CBOs as of December 31, 2019, to 0.95 percent as of September 30, 2023.
Questions or comments? Please contact KC.SRM.SRA.CommunityBankingBulletin@kc.frb.org
